Car fuses are a small but powerful component of your vehicle. They protect the electrical circuits in your car from excessive current that can cause damage.
But what happens when a fuse blows? This article will demystify the topic of blown car fuses.
Contents
Understanding Car Fuses
A car fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits from overload or short circuits.
Automobiles install a safety device known as a fuse to protect electrical circuits from overload and short circuits.
There is a metal strip inside that melts when an excessive amount of current passes through it.
This leads to the circuit breaking, thereby preventing damage to any other components.
Various varieties and ratings of fuses are available to determine the maximum amount of current they can handle before blowing.
Blade fuses are standard on the majority of modern cars.
The glass tubes used in vintage automobiles serve as fuses.
The various ratings, which range from 5 to 40 amps, are easily identifiable thanks to color coding.
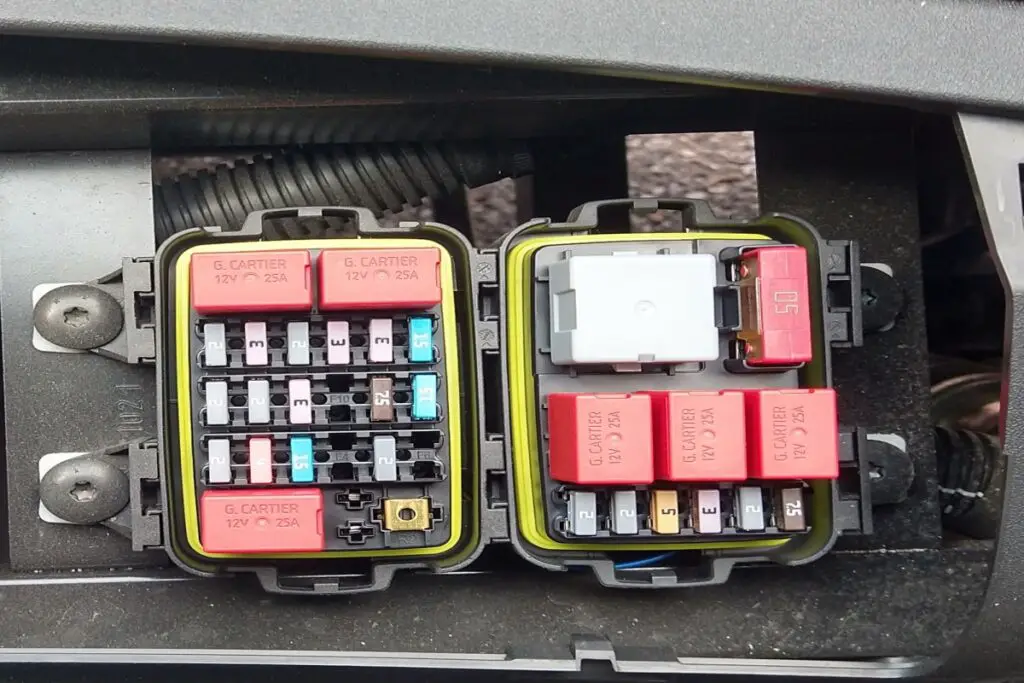

What Does a Blown Car Fuse Look Like?
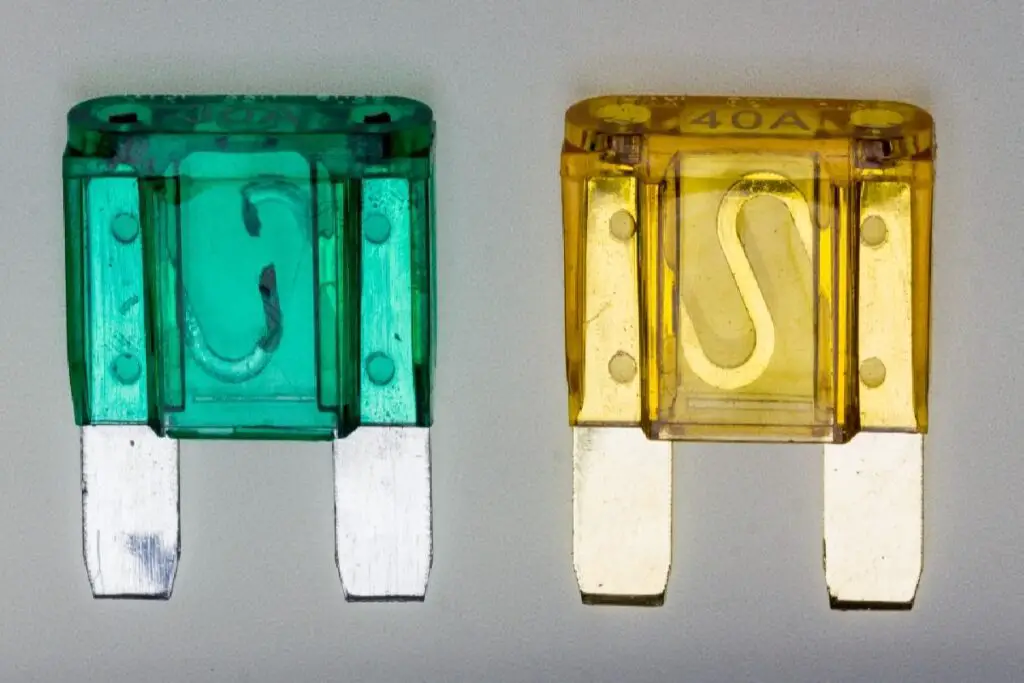
A blown car fuse often has visible signs of damage. The fuse may contain a broken or burned metal strip. In comparison, a functioning fuse will have an intact metal strip.
The metal strip inside is clearly broken or melted.
There may be dark or metallic residue inside.
the plastic casing The plastic may appear slightly warped or discolored.
What might possibly cause my car to melt fuses rather than blow them out?
The fuses in your automobile are similar to safety devices in that they safeguard the electrical circuits in your vehicle.
In the event that there is an excessive amount of electrical current flowing through them, which may occur in the event that there is a short circuit or an overload in the system, they are designed to “blow” or “break.”
Nevertheless, there are instances in which a fuse melts rather than blowing or shattering.
It is possible for this to occur when the electrical current is greater than what the fuse is able to handle, but it is not high enough to cause the fuse to burst instantly.
Instead, the fuse’s temperature rises as a result of the additional current, and if this process is allowed to continue for an extended period of time, the fuse may eventually melt.
Another possible explanation for why a fuse can melt rather than blow is that the connection at the fuse holder is not as strong as it should be.
When electricity passes through a fuse that is not properly seated or that has corroded, resistance can be caused, which results in the generation of heat.
The fuse may melt as a result of this heat over the course of time.
Keep in mind that a fuse that has melted is often an indication that there is an underlying problem with the electrical system of your car that needs to be addressed.
When dealing with problems of this nature, it is always better to seek the advice of a qualified electrician or mechanic.
5 Shocking Signs of a Blown Car Fuse
- Non-working Electrical Components: If a specific electrical component (like your car radio or headlights) stops working, it could be due to a blown fuse.
- Car Won’t Start: Sometimes, a blown fuse can prevent the car from starting.
- Flickering Lights: If your car’s lights are flickering, it might be a sign of a blown fuse.
- Blown Fuse Indicator: Some cars have a fuse indicator that lights up when a fuse blows.
- Visible Fuse Damage: Upon inspection, a blown fuse may show visible signs of damage, such as a broken or burned metal strip.
Common Causes of Blown Car Fuses
When the circuit draws more current than the fuse can handle, the fuse blows. This can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
Electrical overload: Too many devices drawing power simultaneously
Short circuits: damaged wiring causing improper current flow
Incorrect fuse rating: Using a fuse with too low an amperage
Water damage: moisture causes short circuits.
Age and wear: Fuses deteriorate over time.
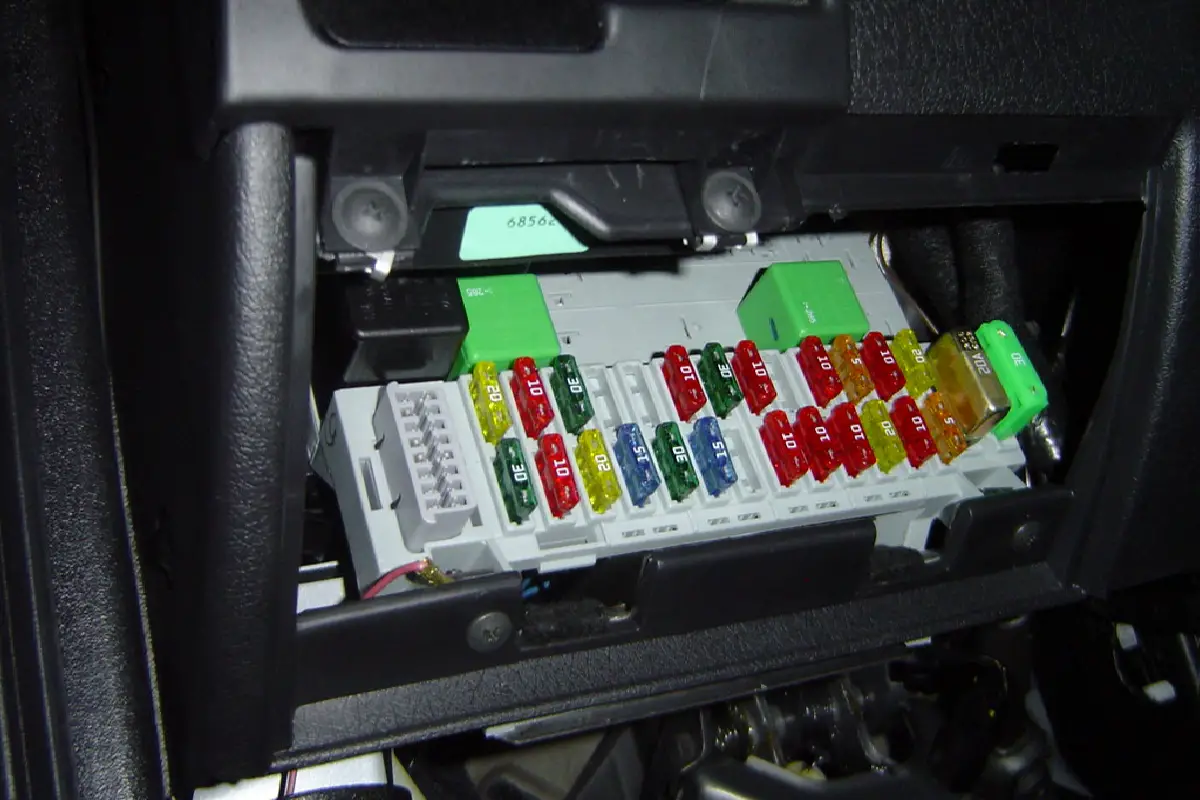
How to Check for a Blown Car Fuse
- Locate the fuse box (usually under the dashboard or in the engine compartment).
- Remove the fuse box cover.
- Use the fuse diagram to identify the relevant fuse.
- Using fuse pullers or needle-nose pliers, carefully remove the fuse.
- Inspect the fuse for signs of damage.
- If the visual inspection is inconclusive, use a multimeter to confirm.
Here is how to use a multimeter
- Set the multimeter to the continuity or resistance setting.
- Touch the probes to both ends of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or shows zero resistance, the fuse is good. If there’s no reaction, it’s blown.
If you don’t have a multimeter, you can perform a basic test:
- Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament.
- You can also swap the suspected blown fuse with a known good fuse of the same amperage to see if the problem is resolved.
If you find a blown fuse, it’s essential to replace it correctly.
- Use the Right Amperage: Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using the wrong amperage fuse can lead to electrical problems or even fires.
- Safety Precautions: Before handling fuses, disconnect the car’s battery to prevent electrical shock or short circuits.
Preventive Measures for Blown Car Fuses
- Regularly inspect the wiring for damage or wear.
- Avoid overloading circuits with aftermarket accessories.
- Keep electrical components dry and protected from moisture.
- When replacing fuses, use the correct fuse rating.
- Address electrical issues promptly to prevent cascading problems.
What is a fuse amp rating?
The amp rating of a fuse measures the maximum electrical current that it can safely handle.
If you use a fuse with an amp rating that’s too low, the fuse might blow prematurely, even if the circuit is operating as it should.
If the amp rating is too high, the fuse might not blow when it needs to, which could lead to an electrical overload and damage your vehicle.
Sometimes, replacing all the fuses at once is unnecessary and expensive. I
If your car is older and hasn’t had its fuses replaced in a while, replacing all of them could help prevent future electrical problems.
However, if the existing fuses are working properly, you don’t need to replace them.
Also, when replacing all fuses at once, you might accidentally use a fuse with the wrong amp rating, which could cause electrical problems.
Generally, it’s best to replace fuses as they blow unless you suspect they’re outdated or faulty.
Always use the correct amp rating for each circuit. Consult a professional mechanic if you’re unsure about anything.

What to Do If Fuses Continue to Blow
If you find yourself repeatedly dealing with blown fuses, it’s essential to address the underlying issues:
- Electrical Shorts: Short circuits can cause fuses to blow repeatedly. Seek professional help to diagnose and fix the issue.
- Professional Assistance: If the problem persists, consult a mechanic or an automotive electrician to ensure there are no hidden electrical problems.
Easy DIY Solutions for a Blown Car Fuse
Changing out a blown fuse in an automobile is a straightforward task.
In addition to a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers, you will need a new fuse that has the same rating as the previous one.
Before replacing a fuse, it is imperative that you always remember to turn off your vehicle and disconnect the battery.
Identify the fuse that has blown.
To replace the fuse, you should buy one that has the appropriate amperage rating.
Replace the old fuse in a safe manner.
After inserting the replacement fuse, check to see that it is firmly seated.
You should test the affected electrical system.
Helpful tools:
- Fuse puller
- Spare fuses
- Flashlight
- Owner’s manual
Consequences of Ignoring a Blown Car Fuse
Ignoring a blown fuse in your vehicle can result in a number of electrical issues, including damage to the electrical system and even the possibility of a fire. In the short term, it is essential to resolve this matter.
There is a potential risk of fire due to overheated circuits.
There are more expensive electrical components that are susceptible to damage.
There are deficiencies in the safety features of the vehicle.
Unexpected mechanical or electrical issues may arise while the driver is on the road.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of car fuses is critical for every driver.
By recognizing the signs of a blown fuse, taking preventive measures, and knowing how to replace them, you can maintain your vehicle’s electrical system effectively.
Remember, prompt attention to electrical issues can save you time, money, and potential safety risks in the long run.
FAQ
Q1. Can you fix a blown car fuse?
Yes, you can fix a blown car fuse by replacing it with a new one of the same rating. It’s a simple process that involves locating the blown fuse in your car’s fuse box, removing it, and inserting a new one. If there is no fuse within range, you can either use a light wire to wrap the two terminals or use the horn fuse to replace it if the car starts.
Q2. How long do car fuses last?
Car fuses typically last for the lifetime of the vehicle, often 10-15 years or more, unless they’re subjected to electrical overloads or short circuits. However, factors like frequent use of high-draw electrical components, exposure to extreme temperatures, or the state of the vehicle’s electrical system as a whole can affect their longevity.
Q3. Can a bad fuse drain a battery?
A bad fuse itself cannot drain a car battery, as a blown fuse breaks the electrical circuit and stops current flow. However, if a fuse is faulty or improperly installed, it might allow a circuit to remain active, potentially leading to a parasitic drain on the battery.
Q4. Can you jump-start a car with a blown battery fuse?
Jump-starting a car with a blown battery fuse is generally not possible or recommended. The battery fuse is designed to protect the charging system, and if it’s blown, it will prevent the battery from receiving or supplying power, making a jump start ineffective and potentially dangerous.
Q5. Does a blown fuse stop power?
A blown fuse does stop power flow in the circuit it protects. When a fuse blows, it creates an open circuit, effectively cutting off the electrical current to prevent damage to components or potential fires.




Leave a Reply