
Did you know that modern vehicles now contain over 100 million lines of code and rely on dozens of interconnected systems to function efficiently? Cars are no longer machines that get us from point A to point B—they’ve evolved into sophisticated technological marvels.
From safety features that protect occupants to infotainment systems that keep us connected, today’s cars are designed to enhance safety, convenience, and performance like never before.
This article is your comprehensive guide to understanding modern car systems like the ones mentioned above.
Whether you’re a new or old driver, learning about these systems will not only make you a more informed driver but also help you maintain your car, improve your driving experience, and ensure your safety on the road.
Contents
1. Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems are the heart of a car’s entertainment and navigation functions.
These systems combine information (like navigation and diagnostics) with entertainment (music, podcasts, and more) to keep drivers informed and passengers entertained.
Components
- Touchscreens: The centerpiece of most infotainment systems, providing an interface for navigation, music, phone calls, and vehicle settings.
- Audio Systems: High-quality speakers and amplifiers deliver an immersive sound experience.
- Navigation Systems: Built-in GPS helps drivers find the best routes.
- Control Units: Embedded systems that process data and manage connectivity.
Features
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Seamless pairing with smartphones for hands-free calls and music streaming.
- Apple CarPlay and Android Auto: Smartphone integration for accessing apps, maps, and messages.
- Voice Control: Allows drivers to operate the system without taking their hands off the wheel.
Benefits
- Easier access to navigation, reducing the risk of getting lost.
- Safer driving with hands-free phone functionality.
- Enhanced passenger experience with entertainment options.
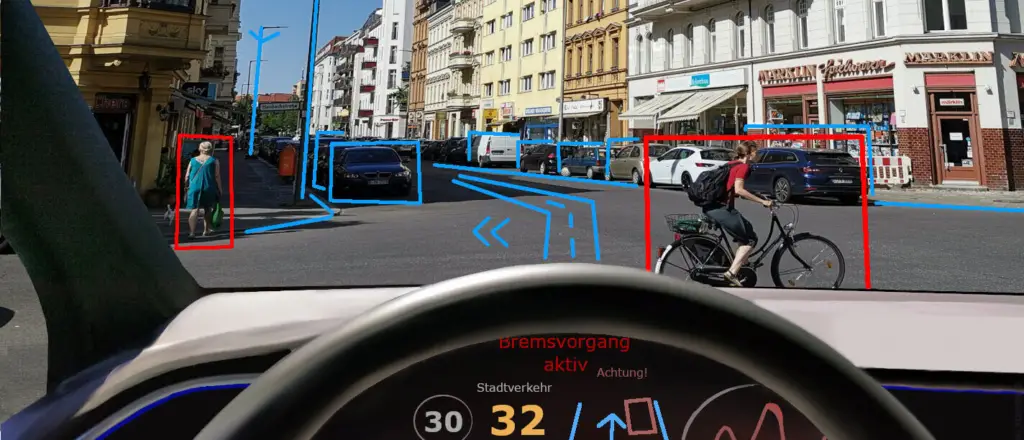
2. Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS is revolutionizing road safety by leveraging technology to assist drivers in avoiding accidents.
These systems use cameras, sensors, and AI to monitor the road and provide real-time feedback or intervention.
Components
- Cameras: Mounted around the car to provide a 360-degree view.
- Radar Systems: Detect the position and speed of nearby vehicles.
- Lidar Sensors: Use lasers to measure distances and detect obstacles.
Features
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Automatically adjusts your car’s speed based on the distance from the vehicle ahead.
- Lane Departure Warning: Alerts drivers if they unintentionally drift out of their lane.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Applies brakes to prevent or mitigate collisions.
- Blind-Spot Monitoring: Notifies drivers of vehicles in their blind spots.
Benefits
- Prevents accidents by providing early warnings or automatic intervention.
- Reduces the stress of driving in heavy traffic.
- Instills confidence in drivers, especially during challenging conditions.
3. Engine Management Systems
The engine management system ensures that your car’s engine operates efficiently and reliably.
It manages the engine’s power output, fuel delivery, and emissions using a network of sensors and actuators.
Components
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The brain of the system, controlling engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Sensors: Monitor parameters like oxygen levels, fuel pressure, and engine temperature.
- Actuators: Devices that execute commands from the ECU, like opening the throttle or adjusting the fuel mixture.
Features
- Fuel Injection: Delivers precise amounts of fuel to optimize combustion.
- Turbocharging: Boosts engine power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): Adjusts the timing of the engine’s valves to enhance performance and efficiency.
Benefits
- Improved fuel economy, saving money on gas.
- Reduced emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Enhanced engine performance and longevity.
4. Transmission Systems
Transmission systems are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the car to move at different speeds while maintaining efficiency.
Components
- gearbox: Changes the gear ratio to suit different speeds and loads.
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission.
- Differential: Distributes power to the wheels, especially during turns.
Features
- Automatic Transmission: Shifts gears automatically, providing a smoother driving experience.
- Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT): Combines the efficiency of manual transmission with the convenience of automatic.
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT): Provides seamless gear transitions for improved efficiency.
Benefits
- Smoother acceleration and driving experience.
- Improved fuel efficiency, especially with CVTs.
- Reduced strain on the engine, leading to a longer vehicle lifespan.
5. Suspension and Steering Systems
Suspension and steering systems play a critical role in ensuring a comfortable and controlled ride. They absorb shocks from the road and allow drivers to steer accurately.
Components
- Shock Absorbers and Struts: Dampen vibrations from the road.
- Steering Rack and Pinion: Converts the driver’s steering input into wheel movement.
Features
- Adaptive Suspension: Automatically adjusts to changing road conditions for a smoother ride.
- Power Steering: Reduces the effort needed to turn the steering wheel.
- Four-Wheel Steering: Enhances maneuverability by allowing all four wheels to steer.
Benefits
- Improved ride comfort, even on bumpy roads.
- Better handling and stability during turns.
- Enhanced driver control, especially at high speeds.
6. Brake Systems
Brake systems are essential for safe stopping and controlling the vehicle during emergencies.
Components
- Brake Pads and Rotors: Create the friction needed to stop the car.
- Calipers: Clamp the brake pads onto the rotors to generate stopping power.
Features
- Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheels from locking during hard braking.
- Electronic Brake-Force Distribution (EBD): Adjusts braking force to each wheel for better control.
- Brake Assist: Increases braking power during emergencies.
Benefits
- Reliable stopping power in all conditions.
- Reduced risk of skidding or losing control.
- Enhanced safety during sudden stops.
7. Electrical Systems
Electrical systems power everything in your car, from the engine to the lights and entertainment systems.
Components
- Battery: Stores electricity to start the car and power electronics.
- Alternator: Generates electricity to recharge the battery and run electrical systems.
Features
- Keyless Entry: Allows you to unlock your car without a traditional key.
- Power Windows: Conveniently open and close windows with the push of a button.
- Lighting Systems: Includes headlights, brake lights, and interior lights.
Benefits
- Enhanced convenience and functionality.
- Reliable power for critical car components.
- Improved visibility and safety with advanced lighting.
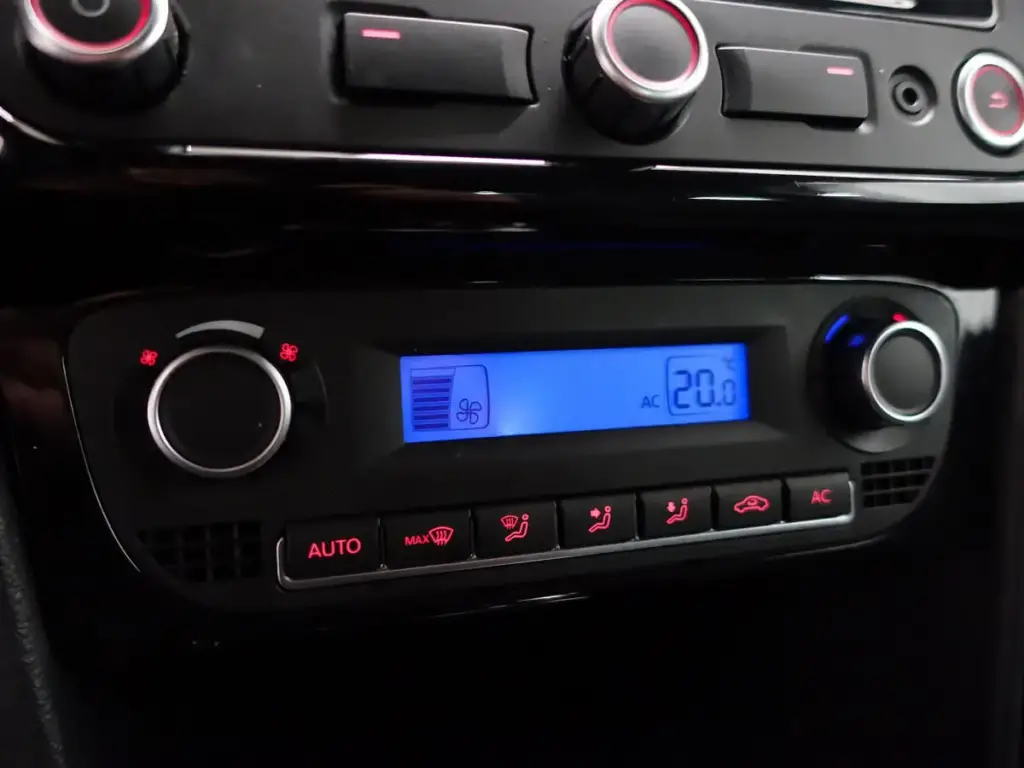
8. Climate Control Systems
Climate control systems regulate the temperature and air quality inside the car, ensuring a comfortable cabin environment.
Components
- Air Conditioning Unit: Cools the air during hot weather.
- Heater: Warms the cabin during cold weather.
- Ventilation System: Circulates air throughout the car.
Features
- Dual-Zone Climate Control: Allows different temperature settings for the driver and passengers.
- Automatic Temperature Control: Maintains a preset cabin temperature.
- Air Purifiers: Improve air quality inside the car.
Benefits
- Greater comfort for all occupants.
- Improved air quality, reducing allergens and odors.
- Customizable temperature settings for personalized comfort.

9. Safety Car Systems
Safety systems protect occupants during accidents and reduce the likelihood of crashes.
Components
- Airbags: Cushion impact during a collision.
- Seat Belts: Restrain passengers to minimize injury.
- Crumple Zones: Absorb and distribute impact forces.
Features
- Pre-Collision Systems: Detect obstacles and prepare the car for impact.
- Pedestrian Detection: Identifies pedestrians and applies brakes if necessary.
- Rollover Protection: Prevents vehicles from tipping during sharp turns.
Benefits
- Reduced risk of severe injury in accidents.
- Increased peace of mind for drivers and passengers.
- Enhanced vehicle safety ratings.
Conclusion
Modern cars are more than just machines—they integrate advanced systems to enhance safety, performance, and comfort.
From infotainment systems that keep you connected to safety systems that protect you during collisions, understanding these features makes you a more informed driver.
Stay curious, stay informed, and make the most of your driving experience. Share this guide with your friends and family to help them understand the incredible technology behind today’s vehicles.




Leave a Reply